Antioxidants
Americans spend several billion dollars a year on antioxidants in an effort to improve their health. Science has been looking at antioxidants and their role in everything from preventing cancer and heart disease to boosting the immune system and slowing the aging process. Antioxidants provide a layer of protection for the cells and tissues of the body, just as a thick coat of wax helps protect a car's finish. Specifically, antioxidants protect against free radical damage. What are free radicals ?
People must breathe in oxygen to live. Continuously on the move in the blood stream and transported to every cell, oxygen is necessary for all essential bodily functions. However, a small amount of this oxygen gets loose and produces unstable by-products called free radicals. Body processes, such as metabolism , as well as environmental factors, including pollution and cigarette smoke, can produce free radicals. An overload of free radicals in the body causes damage to the cells, ultimately resulting in disease and accelerated aging.
Antioxidant-rich food may help prevent various cancers, heart disease, and diseases of aging. Vitamins C and E, carotenoids (including beta-carotene), and the mineral selenium are all powerful antioxidants found in food. Vitamin C, a water-soluble vitamin, is also known as ascorbic acid. Most of the vitamin C in the diet (90%) comes from fruits and vegetables. However, since vitamin C is water soluble, cooking can destroy the vitamin C in a food.
![Cigarette smoke, including second-hand smoke, is a major source of free radicals. These volatile molecules can damage tissues and cause disease. [© 1993 Custom Medical Stock Photo, Inc. Reproduced by permission.]](../images/nwaz_01_img0026.jpg)
Vitamin E, also known as alpha tocopherol, is a fat . Because vitamin E is found in oils, people who follow a low-fat diet may not get enough. Beta-carotene is a member of the carotenoid family. Found mainly in plants, carotenoids provide the vibrant red, yellow, green, and orange colors of fruits and vegetables, with carrots being a major contributor of beta-carotene. Typically, beta-carotene is a conditionally essential nutrient , but when one's intake of vitamin A is low, beta-carotene becomes an essential nutrient, meaning that it must be obtained from food and cannot be manufactured by the body.
Selenium is an essential trace mineral ( trace minerals are needed only in small amounts). The amount of selenium found in food is directly related to the amount of selenium in the soil in which the food was grown. It is necessary for healthy immune function and is tied to killer-cell activity and antibody production. The many health benefits of the various antioxidants can be provided by a variety of food sources.
More and more functional foods contain combinations of various supplements. As popular as antioxidants are, an excess amount of them can be toxic. One reason to obtain antioxidants from food is that high doses may
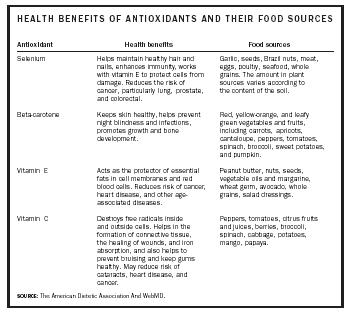
| Antioxidant | Health benefits | Food sources |
| Selenium | Helps maintain healthy hair and nails, enhances immunity, works with vitamin E to protect cells from damage. Reduces the risk of cancer, particularly lung, prostate, and colorectal. | Garlic, seeds, Brazil nuts, meat, eggs, poultry, seafood, whole grains. The amount in plant sources varies according to the content of the soil. |
| Beta-carotene | Keeps skin healthy, helps prevent night blindness and infections, promotes growth and bone development. | Red, yellow-orange, and leafy green vegetables and fruits, including carrots, apricots, cantaloupe, peppers, tomatoes, spinach, broccoli, sweet potatoes, and pumpkin. |
| Vitamin E | Acts as the protector of essential fats in cell membranes and red blood cells. Reduces risk of cancer, heart disease, and other age-associated diseases. | Peanut butter, nuts, seeds, vegetable oils and margarine, wheat germ, avocado, whole grains, salad dressings. |
| Vitamin C | Destroys free radicals inside and outside cells. Helps in the formation of connective tissue, the healing of wounds, and iron absorption, and also helps to prevent bruising and keep gums healthy. May reduce risk of cataracts, heart disease, and cancer. | Peppers, tomatoes, citrus fruits and juices, berries, broccoli, spinach, cabbage, potatoes, mango, papaya. |
| SOURCE : The American Dietetic Association And WebMD. | ||
actually promote free radical production, also known as pro-oxidation, increasing the chance for health problems. Those who may benefit most from antioxidants include people dealing with a lot of stress , dieters limiting their calories to 1,200 per day or less, people on a low-fat diet, smokers, older adults, and people with a family history of heart disease or cancer.
SEE ALSO Functional Foods .
Susan Mitchell
Bibliography
Medical Economics Company (2001). PDR for Nutritional Supplements. Montvale, NJ: Author.
Internet Resources
American Dietetic Association. "Vitamin E: Disease Prevention for Your Good Health." Available from <http://www.eatright.org>
Doheny, Kathleen. "The Supplement Frenzy." Available from <http://www.webmd.com>

Comment about this article, ask questions, or add new information about this topic: