Renewing shiatsu
Shiatsu is a traditional Asian technique involving finger pressure to bring your life energy into harmony. Shiatsu sessions benefit the flow of air in the body and the fight against respiratory infections.

+ Shiatsu originated over 6,000 years ago as a teaching of Chinese medicine. The technique wasn't introduced to the rest of the world until the middle of the 20th century.
Shi means “fingers” and atsu means “pressure”. Shiatsu means “finger pressure” in Japanese. The technique is also called Japanese finger acupressure. Using the rhythmic pressing of acupressure points for short periods, the shiatsu technique is a treatment that works on the meridians of the body to put our chi or life energy in balance. This energy can be either yin or yang (passive-active, negative-positive).
The organs can also be yin or yang. The chi or vital energy should flow harmonically through the organs. When the flow is unbalanced it produces ailments.
The philosophy underlying shiatsu considers that if we eat a healthy diet, breath correctly and maintain a strong and flexible body the chi flows freely, bringing good health.
As with other holistic remedies, shiatsu aims to increase our immune system's ability to cure illnesses in the body by stimulating the flow of the chi. Shiatsu sessions are an excellent treatment for coughs, common colds and asthma.
∎ Nasal congestion and headache.
This massage helps to relieve nasal congestion and headaches. Begin by pinching the eyebrows with the index finger and thumb of both of your hands, starting in the center and then moving toward the temples. Repeat this massage several times.
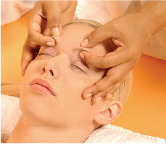
∎ Colds.
A good way to relieve cold symptoms which are making you feel bad is to gently press with your fingertips the area around the eyes.

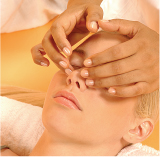
∎ Sinus infections and the flu.
Press with your index and middle fingers on both sides of the nose to help relieve sinus pains caused by sinus infections and the flu.

Comment about this article, ask questions, or add new information about this topic: