Vision Disorders - Treatment
Traditionally, the usual treatment for vision disorders has been fitting the patient with eyeglasses. Eyeglasses consist of glass or plastic lenses set in a
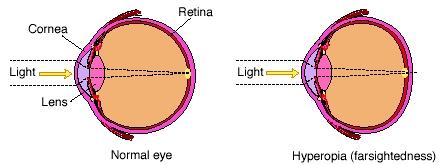
frame. These corrective lenses compensate (make up) for any errors in the patient's cornea and lens. If the patient's lens is too flat, for example, the lenses in the eyeglasses will be more round. Hyperopia, myopia, and astigmatism can all be treated very effectively, easily, and inexpensively with eyeglasses.
Some patients prefer to use contact lenses instead of eyeglasses. The principle behind contact lenses is the same as that behind eyeglasses. In the case of contact lenses, however, the corrective lens is placed directly on the eye.
Many vision disorders can now be treated surgically. An example is radial keratotomy (RK). Radial keratotomy (pronounced RAY-dee-uhl KARE-uh-TOT-uh-mee) is now a common procedure for the treatment of myopia. In RK, a doctor makes very small incisions (cuts) in the cornea to change its shape. The goal is to produce a cornea that has exactly the right shape to produce normal vision.
Traditional RK surgery is done with a very small diamond-tipped blade. Another approach now being studied involves the use of a laser beam to make the necessary incision. By 1999 this procedure had not yet received government approval in the United States for general use.
A form of RK surgery with lasers has been approved for treatment of astigmatism. The procedure is still quite new, however, and a patient should consider the risk carefully before choosing RK surgery.

Comment about this article, ask questions, or add new information about this topic: