Earache - Treatment
Most infections of the ear are treated successfully with antibiotics. The antibiotics kill any bacteria responsible for the infection. If the infection is caused by a virus, the antibiotics are of no value.
The antibiotics can be applied directly to the outer ear in cases of otitis externa. They are often combined with steroids to help reduce inflammation and swelling.
Otitis media is usually treated with oral (taken by mouth) antibiotics. The most popular medications are penicillins and cephalosporins (pronounced seffa-lo-SPORE-inz). They are usually given over a seven to ten day period.
Pain from an ear infection can be relieved by holding a warm compress or a water bottle filled with warm water and wrapped in a towel against the infected ear. Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as aspirin, ibuprofen, and acetaminophen, may also offer some relief from the pain. Children under the age of twelve should not take aspirin as it can cause Reye's syndrome (see Reye's syndrome entry).
Alternative Treatment
Some practitioners believe that food allergies (see allergies entry) increase the risk of ear infections, since allergic reactions can cause the tissues in the middle ear to swell, making it a better environment for bacteria and viruses to thrive. They recommend eliminating foods from the diet that might cause allergic reactions, such as wheat, dairy products, corn, peanuts, citrus fruits, and eggs.
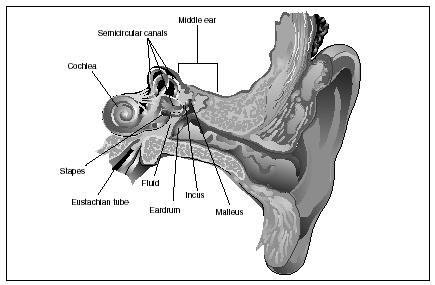
Ear drops that contain herbal products are also recommended for the treatment of earache. Some herbs that have been suggested include goldenseal, mullein, St. John's wort, and echinacea (pronounced ekk-ih-NAY-shuh). Massage therapy of the skull may also be useful in relieving pressure on the ears and improving the functioning of the eustachian tube.

Comment about this article, ask questions, or add new information about this topic: