Cerebral Aneurysm - Diagnosis
The symptoms described may prompt a doctor to order a series of tests for a cerebral aneurysm. The most reliable test is a computed tomography
(CT) scan. In a CT scan, X rays are projected through the brain at various angles. These X rays produce photographs of the brain from different directions. A computer program is then used to combine the pictures, which produces a broad, overall view of the brain. CT scans are also sometimes called computerized axial tomography (CAT) scans.
A CT scan is usually able to determine whether or not an aneurysm exists. It is also able to pinpoint the region of the brain in which the rupture has occurred. To get the clearest result, the scan must usually be done within seventy-two hours after rupture.
If questions remain after a CT scan, follow-up tests might be run. One such test is a lumbar puncture, or spinal tap. In a lumbar puncture, a long, thin needle is used to remove cerebrospinal fluid (CF, liquid surrounding the brain and spinal column) from a patient's spine. The fluid is studied for certain characteristic materials formed when blood products are released in the brain.
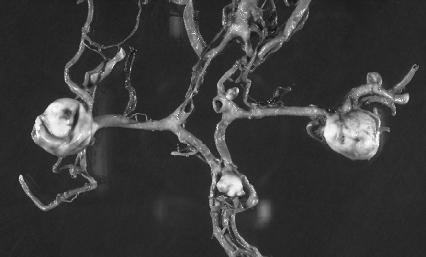
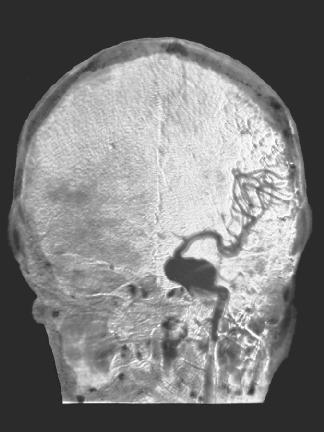
Another follow-up test is a cerebral angiography (pronounced an-gee-AH-graffee). Cerebral angiography is a procedure in which a dye is injected into the blood. The dye is carried throughout the body, including to the brain. An X ray is then taken of the brain. The dye shows the presence of any abnormal structures in blood vessels.

Comment about this article, ask questions, or add new information about this topic: