Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis - Causes
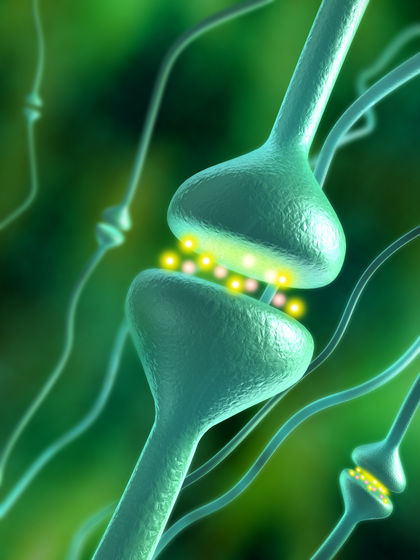
No one knows what causes ALS. One or more factors cause motor neurons in the brain

and spinal cord to begin dying off. Nerve signals can no longer travel from the brain to the muscles. The patient is unable to move normally and he or she becomes weaker. Disturbed nerve messages can cause abnormal muscle movements that result in twitching and spasms. As muscle cells are not used, they begin to die off. The amount of muscle tissue decreases, causing a condition known as wasting.
Researchers have been unsuccessful in finding the cause of motor neuron death. There is some evidence that free radicals may be involved. Free radicals are very active chemicals that can damage living cells. Defective enzymes may also be a factor in the death of motor neurons. An enzyme is a naturally occurring chemical needed for many chemical reactions that occur in the body. Additional research is now being conducted to find out more about the cause or causes of ALS.
Two major forms of ALS are known: familial and sporadic. About 10 percent of all ALS cases are familial. As the name suggests, familial ALS is thought to be caused by genetic factors. Scientists have found that 15 percent of the people with familial ALS have a mutation (change) in a gene known as SOD-1. A parent with this mutated gene can pass it on to his or her children.
Sporadic ALS has no known cause. Certain chemical factors in the body, such as free radicals, may be involved. Or it, too, may result from genetic factors.

Comment about this article, ask questions, or add new information about this topic: